What drives demand for Bitcoin?
Miners earn incentives from mining the blocks of verified transactions, whereas Bitcoin owners benefit from increased Bitcoin prices. Back in 2009, the Bitcoin price suffered high volatility as a near-valueless currency. However, throughout years of development, the value exceeded $19,000 in 2017. After that, Bitcoin lost 76% of its market value but bounced back after, reaching the $30,000 mark in 2020.
Bitcoin encourages early adoption because it is coded to produce only 21 million Bitcoins. The nodes on the network enforce the supply limit encoded in Bitcoin’s source code. Therefore, Bitcoin’s core value proposition resides within its code, making it a scarce resource because it is very difficult to increase its supply.
Bitcoin’s decentralized governance model also prevents other individuals from controlling the network. Besides, the incentive system and governance model protect Bitcoin’s hard cap against changes. For example, miners, specifically, are strongly incentivized not to make changes to Bitcoin’s existing hard cap. Theoretically, miners can change the hard cap (as Bitcoin is just code), but the consequences would be catastrophic. People would lose trust in the Bitcoin network, which would cause Bitcoin prices to crash irreversibly. As a result, miners’ losses in fiat terms would have exceeded the revenue in Bitcoin terms because almost all miners pay their costs in fiat. The costs include equipment costs, salary, energy bills to maintain the Bitcoin network.
Bitcoin’s decentralized governance model also prevents other individuals from controlling the network. Besides, the incentive system and governance model protect Bitcoin’s hard cap against changes. For example, miners, specifically, are strongly incentivized not to make changes to Bitcoin’s existing hard cap. Theoretically, miners can change the hard cap (as Bitcoin is just code), but the consequences would be catastrophic. People would lose trust in the Bitcoin network, which would cause Bitcoin prices to crash irreversibly. As a result, miners’ losses in fiat terms would have exceeded the revenue in Bitcoin terms because almost all miners pay their costs in fiat. The costs include equipment costs, salary, energy bills to maintain the Bitcoin network.
There are two factors that affect Bitcoin supply, the halving of block rewards and the hard cap.
- Halving of the block rewards: The halving of block rewards is another protocol that slowed Bitcoin’s circulation, causing its growth rate to reduce. The slowed circulation has allowed demand to exceed the supply. As a result, prices tend to increase significantly after halving.
- Hard cap: The number of Bitcoin to ever exist will be decided by its system, ultimately affecting supply. When Bitcoin reaches 21 million, mining activities will no longer continue because no new Bitcoin will be created. As of June 2022, Bitcoin supply has reached over 19.058168 million, amounting to 90.75% of the available Bitcoin supply.
What Is the Outlook for Bitcoin Supply?
The Bitcoin supply is currently around 19.058168 million, with its maximum supply capped at 21 million coins. Though, the actual Bitcoin available for trade is much lower. An expert claims that three million of Bitcoin, which takes up around 16% of the circulating supply could be gone because of the users that lost their private keys and hard drives. Besides, the founder of Bitcoin has also not touched the 1.125 million Bitcoin (BTC) he mined to this day. Interestingly, this takes another 6% off the available supply of Bitcoin.
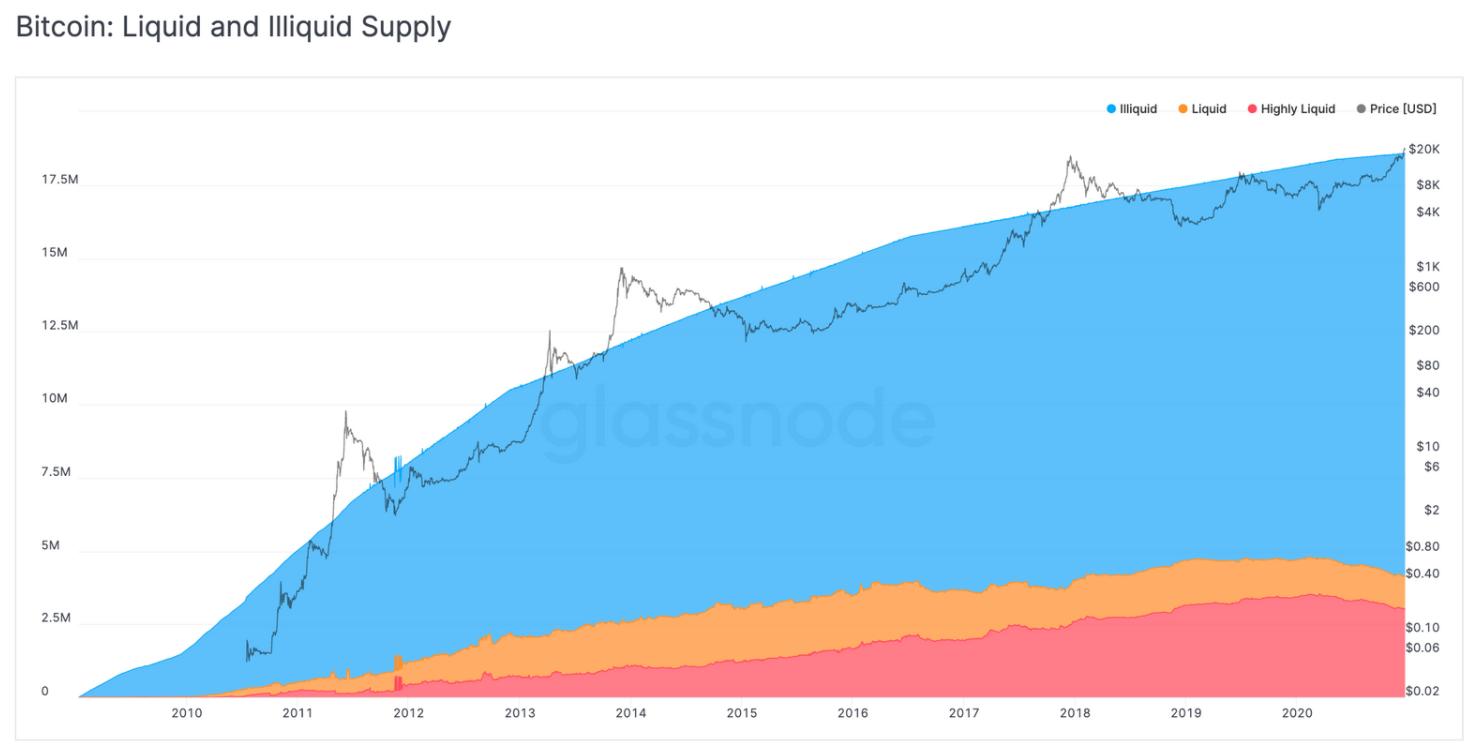
The figure above demonstrates the state of Bitcoin’s liquidity in the market. The state of Bitcoin is categorized into illiquid, highly liquid, and liquid. The blue area represents illiquid Bitcoin (14.5 million). The highly liquid BTC available is only three million. Furthermore, liquid Bitcoin is 1.2 million. Conclusively, the circulating Bitcoin supply that is no longer liquid is around 78%. There are only 4.2 million BTC (22%) currently in circulation and available for trading. For over a year, the trend of illiquidity has prevailed, indicating that a significant amount of illiquidity is driving the bullish signal. This is reminiscent of the scenario during the bull run of 2017, where the illiquid supply exceeded the total circulating supply.
What is driving current demand for Bitcoin?
While demand continues to surge, Bitcoin prices will also follow suit, leading to much higher prices. However, despite the demand spike, Bitcoin’s supply rate is not responsive due to Bitcoin’s protocol that slows down Bitcoin mining. We now look at the drivers behind this momemtum.
- Tightening demand: Bitcoin is therefore intrinsically volatile, not because of its scarcity or its finite nature but because of its inflexibility. As the size of its market increases we might find its price swings becoming less frequent but much larger. While bitcoin’s supply remains inelastic, its price will remain subject to change without warning. Reinforcing the above, the growth in desirablility along with the ever tightening highly liquid and liquid portions of Bitcoin add to it's inflexibility and as a result adds to its value as a very desirable investment asset.
- Increased utility as payment: More institutions are accepting Bitcoin as payment. Institutional adoption of Bitcoin as payment has made the cryptocurrency more attractive due to its increased utility as money and investment in traditional exchanges.
- Institutional investor demand: Major market participants such as Circle, Microstrategy, PayPal and Grayscale Bitcoin Trust (GBT), to mention a few, purchase a large number of Bitcoin due to high investor demand. More financial products that utilize Bitcoin as an underlying asset are also being introduced to the market, including exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and other derivatives. For example, the Grayscale Bitcoin Trust (GBT) currently possesses around 3% of the total available supply. The company has been adding Bitcoin to its corporate balance sheet for the last three years. Microstrategy substituting is USD treasury holdings for BTC has spent around $4 billion acquiring Bitcoin at an average price of $32,000. PayPal has also introduced Bitcoin trading to its US users. As institutional investors invest their resources accordingly based on their evaluation of Bitcoin, this is having a subsequently reduction in Bitcoins price volatility.
- More Bitcoin-related Services: Several banks are authorized to offer cryptocurrency services such as deposit-taking, custody, and fiduciary services to the public. Other companies like Utrust from Braga, Portugal have built infrastructure to allow Web2 and Web3 applications make crypto payments via new crypto payment gateways.
- New Tax and Regulation of Crypto: Bitcoin is considered a property that creates capital gains and losses. Besides, the cryptocurrency is imposed with favorable tax treatment, which is beneficial for long-term Bitcoin owners. With Bitcoin’s functionality, relevant authorities have developed regulations and infrastructure to accommodate it. Bitcoins assets classification recogniition will pay an important role as the entire Web3 space matures. However, as we have seen in China, authorities have outlawed Bitcoin mining in 2021 which merely caused mining infrstrucutre to find new homes elsewhere in the world such as North American, South America, the Middleeat and Europe. Authorites are also debating over Bitcoin’s asset classification should be altered, leaning towards either securities or a commodity. This uncertainty could affect future regulation imposed on Bitcoin, potentially affecting Bitcoin prices. However being a decentralised solution, like physical precious metals, outside the control of any centralised authority Bitcoin has and simple will continue to be adopted globally with or without the participation of the legacy finanical system and its regulators. It is a soverign open source technology supporting the soverign rights of every human being to choose for themselves.
- Legal tender: Inflation and mass fiat currency printing (quantative easing) of all major world currencies accelerates even more so since the recent global lockdowns and especially with respect to the world global reserve currency, the US doller. other smaller nation-states with weaker economies and do not have their own legal tender are increasingly seeking alternatives to avoid fiat currencies disadvantages. The rising awareness about cryptocurrencies has caused these nation-states with weaker economies to consider Bitcoin as a legal tender. Recently, the Central American nation El Salvador and the Central African Republic accepted Bitcoin as legal tender. The Swiss Cantons of Zug and Luganohave adopted Bitcoin as ‘de-facto’ Legal Tender within their cities. For instance, residents of these Cantons have the choice to pay their annual tax bills to the Canton in Bitcoin and Ethereum. With the competition between Swiss Canton’s, regulatory dynamism is always higher then in the rest of Europe. Switzerland has already successfully established a flourishing bitcoin industry with reputable companies. Finally, it is expected that other counties like Paraguay, Ecuador or even Argentina may take the step to make Bitcoin legal tender soon.
Conclusion
Bitcoin’s growth has been volatile but is considered a reliable store of value and a hedge against inflation. The capped supply and halved block rewards are two factors that slow down the circulating supply. Despite Bitcoin’s volatile growth, large institutions remain bullish about its growth. Once the block rewards are halved again in 2024, Bitcoin will exceed gold as a store of value. Bitcoin available for trade is much lower and is increasingly illiquid due to big institutions that are buying and holding the cryptocurrency. Despite the limited supply, financial institutions are introducing Bitcoin-related services for smaller investors and investment firms, which will increase Bitcoin utility.








